Cancer Classification

What is cancer?
Nowadays, the classification of cancer is mainly based on the cell type of the tumor-derived tissue and its biological behavior. In pathology, tumors in each system are classified. According to the development of the tumor, it can be divided into: benign tumor and malignant tumor. Benign tumors grow in the original place and will not spread to other parts of the body without endangering life. However, if it keeps proliferating, it may compress adjacent organs and become malignant tumors
Cancer is a common name for a series of related diseases. In a normal healthy human body, cells will grow and divide according to the needs of the body. When cells age or become damaged, they die and are replaced by new cells. However, in people with cancer, their cells divide uncontrollably and spread to neighboring tissues.

Cancer classification by stage
Cancers are classified individually according to their stage. There are several types of staging methods. The most commonly used method uses classification in terms of tumor size (T), the degree of regional spread or node involvement (N), and distant metastasis (M). This is called the TNM staging. Stages can be divided according to the TNM staging classification. Cancer is usually divided into stage 0, to stage IV, and stage IV is the most serious. The basis of staging is the size and spread of the tumor as below:
Stage 0: carcinoma in situ(in its place) abnormal cells are growing in their normal place.
Stage I: cancers are localized to one part of the body. Stage I cancer can be surgically removed.
Stage II: cancers are early locally advanced. Stage II indicates affected lymph nodes on only one side of the organ. Cancer can be treated by chemotherapy, radiation, or surgery.
Stage III: cancers are also late locally advanced. Stage III indicates affected lymph nodes above and below the organ. Cancer can be treated by chemotherapy, radiation, or surgery.
Stage IV: cancers have often metastasized and spread to other organs or throughout the body. Stage IV cancer can be treated by chemotherapy, radiation, or surgery. Despite treatment, a patient's mortality rate can be significantly higher with Stage IV cancer.
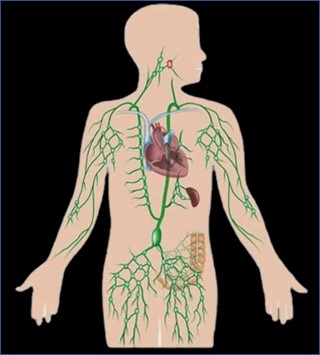
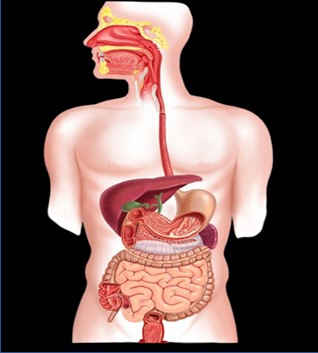
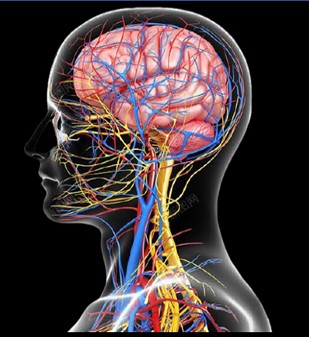
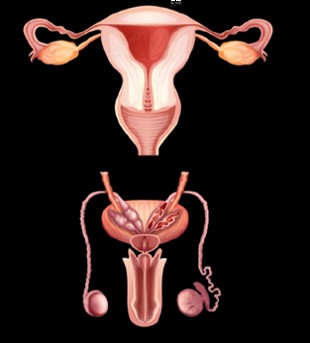
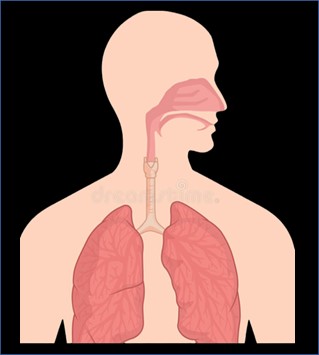
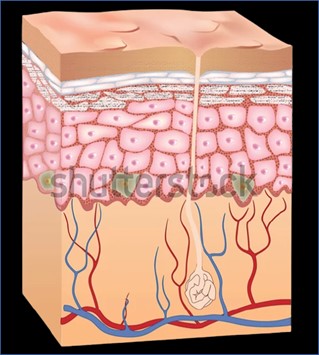
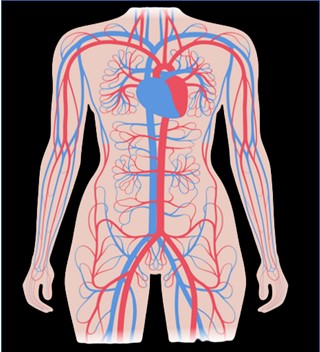
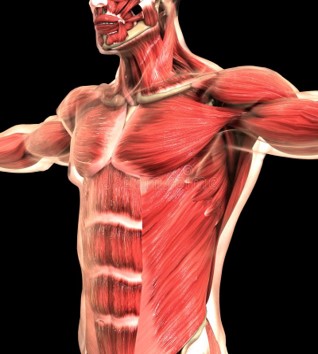
Human Body System Cancer Types
The smallest unit that makes up the human body is the cell. When the cell differentiates into tissue, the tissue and organ form a system, and all systems form a living body. Among them, the organs are grouped together according to a certain model, and the structure that completes the physiological functions together is called a system. According to their functions, the human organs can be divided into 12 systems such as lymphatic immunity, digestion, endocrine, cranial nerves, reproduction, respiration, skin, cardiovascular circulation, muscles, bones, urinary and vision etc. Please check below items.

 EN
EN